At the most basic level schizophrenia is best conceptualized as – At the most basic level, schizophrenia is best conceptualized as a complex mental disorder characterized by disturbances in thought, emotion, and behavior. It is a severe and chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide, and its symptoms can range from mild to severe.
This article will provide an overview of schizophrenia, including its definition, etiology, manifestations, treatment, and prognosis.
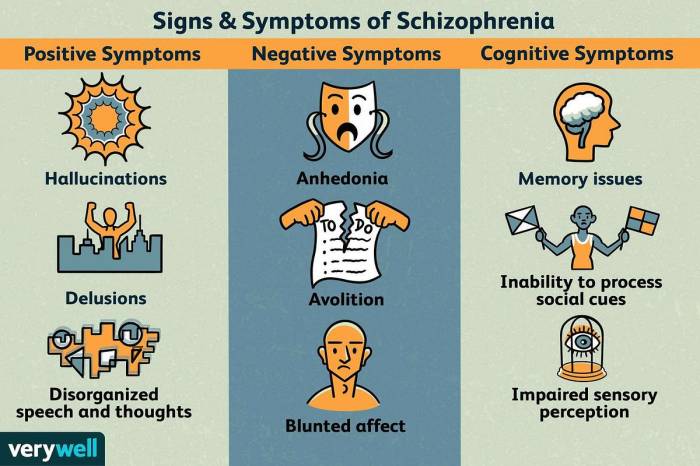
Schizophrenia is a complex and multifaceted disorder, and there is no single, universally accepted definition. However, most experts agree that schizophrenia is a mental illness that affects the way a person thinks, feels, and behaves. People with schizophrenia may experience hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and impaired social functioning.
Definition of Schizophrenia: At The Most Basic Level Schizophrenia Is Best Conceptualized As

Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder that affects a person’s thoughts, emotions, and behavior. It is characterized by a range of symptoms, including hallucinations, delusions, disorganized speech, and impaired social functioning. Schizophrenia is a chronic condition, but with proper treatment, people with the disorder can live full and productive lives.
The core characteristics of schizophrenia include:
- Hallucinations: Seeing, hearing, or smelling things that are not there.
- Delusions: Believing things that are not true, even when presented with evidence to the contrary.
- Disorganized speech: Speaking in a way that is difficult to understand, or using words that do not make sense.
- Impaired social functioning: Having difficulty interacting with others, or withdrawing from social situations.
Etiology of Schizophrenia
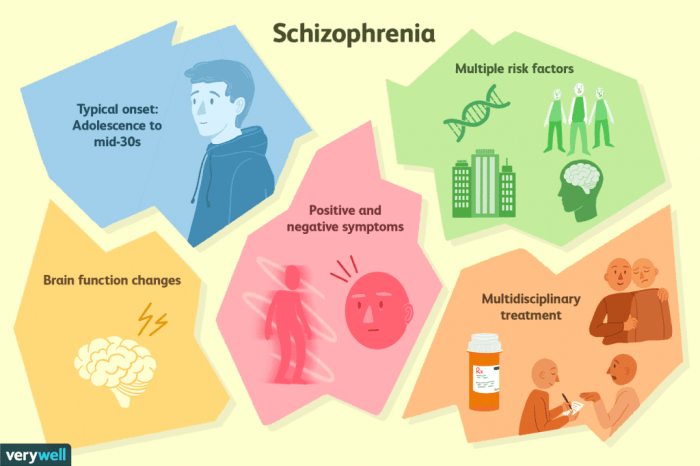
The exact cause of schizophrenia is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Genetic factors play a significant role in the development of schizophrenia. People who have a family history of the disorder are more likely to develop it themselves. However, having a family history of schizophrenia does not guarantee that a person will develop the disorder.
Environmental factors also play a role in the development of schizophrenia. These factors include:
- Prenatal exposure to certain toxins, such as alcohol and drugs.
- Childhood trauma or abuse.
- Stressful life events.
Neurotransmitters are chemicals that help nerve cells communicate with each other. Imbalances in certain neurotransmitters, such as dopamine and glutamate, are thought to play a role in the development of schizophrenia.
Brain abnormalities have also been linked to schizophrenia. People with the disorder often have structural and functional abnormalities in the brain, particularly in the areas responsible for thinking, emotion, and behavior.
Manifestations of Schizophrenia, At the most basic level schizophrenia is best conceptualized as
There are different types of schizophrenia, each with its own unique symptoms. The three main types of schizophrenia are:
- Paranoid schizophrenia: This type of schizophrenia is characterized by delusions of persecution or grandeur. People with paranoid schizophrenia may also experience hallucinations, but they are usually less severe than the delusions.
- Disorganized schizophrenia: This type of schizophrenia is characterized by disorganized speech and behavior. People with disorganized schizophrenia may also experience hallucinations and delusions, but they are usually less severe than the disorganized symptoms.
- Catatonic schizophrenia: This type of schizophrenia is characterized by a lack of movement and speech. People with catatonic schizophrenia may also experience hallucinations and delusions, but they are usually less severe than the catatonic symptoms.
The symptoms of schizophrenia can vary in severity from person to person. Some people may experience only mild symptoms, while others may experience severe symptoms that can interfere with their daily lives.
Schizophrenia can also have a significant impact on a person’s cognitive functioning, social interactions, and daily life. People with schizophrenia may have difficulty with memory, attention, and problem-solving. They may also have difficulty interacting with others and maintaining relationships. Schizophrenia can also make it difficult to hold a job or go to school.
Treatment of Schizophrenia
There is no cure for schizophrenia, but there are treatments that can help to manage the symptoms of the disorder. The main treatments for schizophrenia are medication and psychotherapy.
Antipsychotic medications are the most common treatment for schizophrenia. These medications can help to reduce hallucinations, delusions, and other symptoms of the disorder. Antipsychotic medications are typically taken orally, and they can be effective in reducing the symptoms of schizophrenia by up to 50%.
Psychotherapy is another important treatment for schizophrenia. Psychotherapy can help people with schizophrenia to learn how to manage their symptoms and to live fulfilling lives. There are different types of psychotherapy that can be used to treat schizophrenia, including cognitive-behavioral therapy, family therapy, and social skills training.
In addition to medication and psychotherapy, there are other treatments that can help to manage the symptoms of schizophrenia. These treatments include:
- Supported employment: This program helps people with schizophrenia to find and keep a job.
- Supported housing: This program helps people with schizophrenia to find and keep a place to live.
- Case management: This program helps people with schizophrenia to access the services and support they need.
Prognosis and Recovery from Schizophrenia
The prognosis for schizophrenia varies from person to person. Some people with schizophrenia are able to live full and productive lives, while others may experience more severe symptoms that can interfere with their daily lives.
The factors that influence the prognosis of schizophrenia include:
- The severity of the symptoms.
- The age of onset.
- The person’s social support system.
- The person’s access to treatment.
There are many examples of successful recovery from schizophrenia. With proper treatment and support, people with schizophrenia can live full and productive lives.
FAQ Compilation
What is schizophrenia?
Schizophrenia is a complex mental disorder that affects the way a person thinks, feels, and behaves. It is a severe and chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide.
What are the symptoms of schizophrenia?
The symptoms of schizophrenia can vary from mild to severe. Some of the most common symptoms include hallucinations, delusions, disorganized thinking, and impaired social functioning.
What causes schizophrenia?
The exact cause of schizophrenia is unknown, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
How is schizophrenia treated?
Schizophrenia is treated with a combination of medication and therapy. Medication can help to control the symptoms of schizophrenia, and therapy can help people with schizophrenia to learn how to manage their symptoms and live independently.
What is the prognosis for schizophrenia?
The prognosis for schizophrenia varies from person to person. Some people with schizophrenia are able to live full and productive lives, while others may experience more severe symptoms that require ongoing treatment.